Customer Segmentation How-To: 26 Easy Ways to Segment Customers
As a company’s client base grows, it can become challenging to keep up with each client on an individual level. Customer segmentation can help your team feel more organized while maximizing productivity, interaction efforts, and increasing retention. To help, we will share the most effective strategies, with examples to segment customers.
Table of Contents
- Customer Segmentation Definition
- 26 Easy Ways To Segment Customers and Users (With Examples)
- 1. Determine the Area of Most Value
- 2. Target Age-Specific Audiences
- 3. Be Gender-Specific
- 4. Consider Consumer Income
- 5. Identify Pain Points & Desired Outcomes
- 6. Pick A Niche Market
- 7. Consider Family Status
- 8. Group Consumers Based On Ethnicity & Religion
- 9. Create Campaigns According To Professions
- 10. Consider Location
- 11. Segment Clients According To User Status
- 12. Recommend Climate-Based Products
- 13. Don’t Ignore Birthdays
- 14. Cart Abandonment
- 15. Device Type
- 16. Re-engage Inactive Customers
- 17. Start Segmentation At Entry Level
- 18. Implement Welcome Automation For New Customers
- 19. Send Behavior Triggered Emails
- 20. Apply Lifestyle Segmentation
- 21. Reward Top Purchasers & Repeat Customers
- 22. Use the Three-Bucket Approach
- 23. Utilize Analytics
- 24. Go Beyond The Data
- 25. Always Value Psychographics
- 26. Forecast Ahead
- Understanding Customer Segmentation Models
- Tips on Doing Customer Segmentation
- Customer Segmentation Benefits to Your Business
- Wrap-Up
- PIN THIS FOR LATER…
Customer Segmentation Definition
Customer segmentation involves grouping existing and potential clients of a given market into discrete groups (segments) to deliver more relevant experiences. The division is based on individuals with the same characteristics, behaviors, necessities, and purchasing qualities.
Customer segmentation empowers an organization to better understand each segment’s needs, preferences, and buying patterns. The company can then tailor their efforts to reach clients most fittingly.
Segmentation permits a company to utilize clear-cut correspondence channels to communicate with targeted groups about their product or service. It attracts clients, improves their likelihood of purchasing an item, and boosts customer loyalty and conversations.
For example, a company attempts to attract youthful clients using social media while attracting older clients through radio promotion.
26 Easy Ways To Segment Customers and Users (With Examples)
1. Determine the Area of Most Value
Customer segmentation may vary from industry to industry or the nature of the organization (ex., start-up versus mature companies). Each business must determine where it can derive the most value, be it by size, sector determination, or consumer potential.
After determining the goal, the segmentation model will follow (demographic, geographic, behavioral, etc.).
2. Target Age-Specific Audiences
Consumer needs and preferences continually change with age. Target age-specific audiences by creating segments according to age ranges (babies, children, teens, adults, and seniors) or generation groups (baby boomers, Gen X, millennials, or Gen Z).
For example, target a segment of young Gen Z consumers with a chic fashion line at irresistible discounts that end right before school starts.

3. Be Gender-Specific
Men and women exhibit different needs, interests, and shopping behaviors. Gender-specific marketing will increase engagement. Target specific gender groups and ensure the campaign promotes relevant products and experiences.
For example, Shein created a Facebook ad specifically for women, including the term “for women” in the description to increase engagement and click-throughs.

4. Consider Consumer Income
Income segmentation allows you to measure consumers’ income range and buying power. There’s no point in targeting consumers that cannot afford your product. Use income data to sell different categories or classes of the same product to people based on their income status.
For example, a luxury car manufacturing company should target high-income groups with high-tech, premium cars. However, they should avoid overshooting consumers of a low or medium-income group who cannot afford the product.
5. Identify Pain Points & Desired Outcomes
Segmenting clients according to their pain points and desired outcomes will help you maximize your efforts. After segmenting consumers, develop attractive solutions to increase customer retention.
For example, a car dealership attempts to sell a sedan with multiple warranties that increase the initial price by several thousand dollars. However, competing dealerships include a similar warranty at no extra charge. The car dealership realizes it is losing business due to a financial pain point and, therefore, changes the pricing structure.
6. Pick A Niche Market
Select a niche market that undoubtedly needs your product or service. Then, create a retention strategy to enable customer loyalty and recurring sales.
For example, the total expenditure on pet products in the United States alone was $136.8 billion. There are great opportunities to develop a niche within the pet market, including organic food, treats, toys, flea and tick repellants, GPS trackers, beds, and more.

7. Consider Family Status
Family status is instrumental in segmentation. When a family’s structure and dynamics change, the needs, desires, and buying habits do too, which strongly impacts your sales process.
Categorize clients based on marital statuses, family structures (with or without kids, and how many), and their life stages.
For example, large families may desire bulk or low-income products, while single individuals or couples without kids may prefer luxury purchases.
8. Group Consumers Based On Ethnicity & Religion
An increase in international organizations and global advertising increases the need for demographic segmentation based on culture, ethnicity, and religion. Many of these groups have conflicting beliefs, interests, attitudes, and preferences, which impact their response to marketing strategies and buying habits.
For example, McDonald’s adjusts its menu and advertisements based on regional taste preferences and religious beliefs. India predominantly practices Hinduism, and due to their religious reverence for cows, McDonald’s focuses on advertising vegetarian and non-red meat options.
9. Create Campaigns According To Professions
Use the jobs and professions of customers to apply demographic segmentation to create highly targeted, appealing campaigns.
For example, HomeChef created an email campaign focused on providing teachers and nurses generous discounts.
10. Consider Location
Segment your audience using countries, cities, or specific zip codes.
For example, if you have an online store serving multiple locations, send a virtual “hello” with a photo of the local branch and its employees to create a personal customer experience.
11. Segment Clients According To User Status
Use the behavioral segmentation method to group clients according to their user statuses, like non-users, prospects, first-time buyers, regular users, or defectors.
For example, send a marketing campaign to non-users about why they need your product or send regular users a great supplemental product or service you offer.
12. Recommend Climate-Based Products
Set up a weather- or climate-based segmentation model and market relevant products based on the group’s climate region or season.
For example, a retail company should market swimwear brands to consumers in warmer climates and winter apparel to colder areas.
13. Don’t Ignore Birthdays
Group consumer profiles by age and birth date and send targeted marketing content on their birthday.
For example, email an automated, direct mail to your customers on their birthday with a deeper discount than usual to retain customer loyalty and satisfaction.
14. Cart Abandonment
Almost 70% of desktop users abandon their carts before competing for their purchase. Companies can try reducing the issue by retargeting the users with a series of relevant emails, pop ups, and text messages. Segment consumers according to their activity level and type of product added to their cart.
For example, send an email notifying hesitant customers that their cart will expire after 3 days. Alternatives use popups to inform them if they have added items $100, $200, or more.

15. Device Type
57% of web traffic in the United States comes from mobile phones and tablets, providing an excellent opportunity for segmentation.
For example, a company selling phone accessories should segment its audience based on the type of phone they’re using and target consumers with specific offers.
16. Re-engage Inactive Customers
Use psychographic customer segmentation to re-engage with idle customers that haven’t bought anything recently. You can use an email flow and create a retargeting campaign to create a sense of urgency or FOMO. You can also use “most viewed products” to target inactive customers.
For example, send an automated email to customers that have been inactive for 30 days saying something like “Hey, we’ve missed you.”
17. Start Segmentation At Entry Level
Initiate segmentation at the entry-level by greeting first-time visitors or customers making their first purchase with an exclusive offer. If prospective clients respond to the offer, regroup them into a drip campaign that increases engagement.
For example, give first-time customers a freebie or exclusive discount on their first purchase.
18. Implement Welcome Automation For New Customers
Send an automated welcome email series flow to new customers. The emails are to create brand awareness, build trust and a relationship, and increase customer engagement.
For example, send your welcome series emails over several days or weeks. A sequence example looks like this:
#1: Welcoming email (sent after signup)
#2: Introduction to the company or brand (sent several days after signup)
#3: Showcase your products and services (sent around one week after signup)
#4: Ask for feedback (sent a couple weeks after signup)
#5: Special offers and discounts (sent periodically)
19. Send Behavior Triggered Emails
Segment consumers into groups based on their behavior towards specific products or services. Create automated email marketing campaigns to trigger users’ behavior and engage with them. Website visitors need to log into the site for you to track their behavior.
For example, if a customer downloads a resource on your website, send an automated campaign after 2 hours with additional relevant content.
20. Apply Lifestyle Segmentation
Use demographic and behavioral segmentation to group consumers according to their lifestyle interests.
For example, Nike creates different marketing ads for other segment groups with varying interests, like running, soccer, and tennis. The company creates a different product and marketing campaign for each group.
21. Reward Top Purchasers & Repeat Customers
Create a segment list based on loyal and recurring customers with strong purchasing habits. Then, target your top purchasers with exclusive offers and rewards programs to make them feel special. You can do the same for repeat customers.
For example, rewards top purchasers with incentives to motivate them to add additional products to their carts.

22. Use the Three-Bucket Approach
Segment clients into a short-, medium, – or long-term value bucket. Use the information to determine how much marketing, resources, and engagement you require for each segment.
For example, if a business spends all their time and resources attracting short-term customers, they will lose on greater returns from long-term customers.
23. Utilize Analytics
Even if your customers’ needs are similar, their purchasing habits will differ. Create a different engagement strategy for every buying process using analytics to segment customers according to demographics and purchase habits.
For example, some clients prefer online shopping while others prefer in-person visits. Create a separate marketing campaign to reach each group.
24. Go Beyond The Data
Data is crucial to implement a customer segmentation strategy. However, you must go beyond data collection to attract and retain customers. Ensure your segmentation strategy includes relevant engagement activities that truly speak to each customer.
For example, create personal communication and touchpoint experiences that cater to each client. It should create a moment of “they get me.”
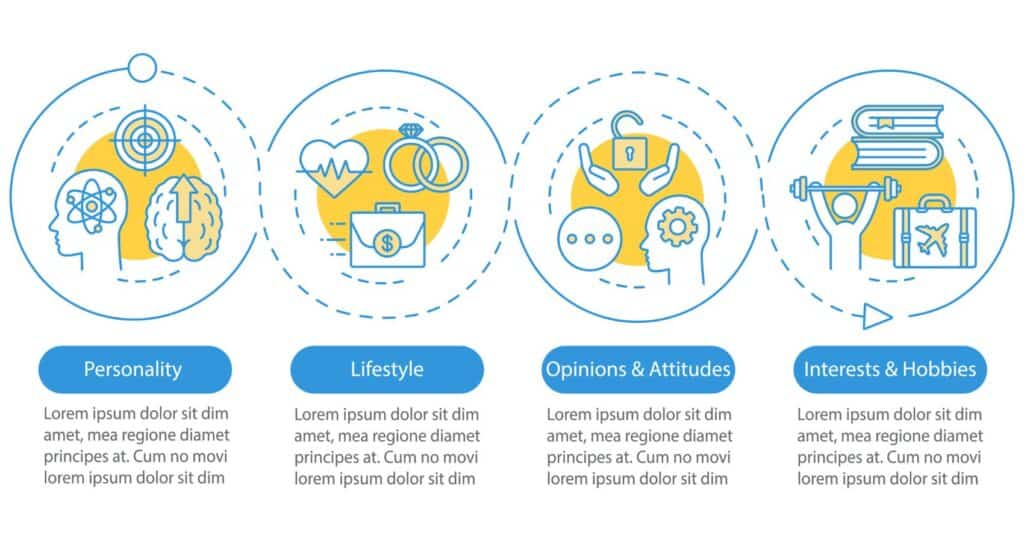
25. Always Value Psychographics
Segmenting clients according to demographics like age, gender, and occupation is fundamental for a compelling business structure. However, psychographics like life phases, pains, desires, and behavioral patterns are more critical. Two consumers with the same gender and profession can have opposite behavioral patterns, making one a top client and the other your worst client.
For example, use surveys, review calls, and monitoring online activity like social media and purchase behaviors to gather psychological information about consumers.
26. Forecast Ahead
Cast your segmentation nets into the future to determine what other products your customers will be interested in purchasing a couple of years from now.
For example, ask current clients who would be interested in trying a new spin-off product.

Understanding Customer Segmentation Models
A customer segmentation model is a specific method of dividing a company’s customer base into groups based on shared characteristics relevant to marketing, including age, gender, location, income, interest, and spending habits.
The type of customer segmentation model depends on the types of customers you plan to target. There are 4 primary models you can use to improve conversion: Demographic, Geographic, Behavioral, and Psychographic Customer Segmentation.
However, regardless of your selected approach, useful segmentation must include the following six characteristics:
- Identifiable: Customers and their characteristics need to be identifiable in each segment.
- Substantial: Each segment needs to be large enough to be profitable.
- Accessible: The company needs access to appropriate communication and distribution channels to reach its segments.
- Stable: A segment must be stable long enough for marketing efforts to be successful.
- Differentiable: Customers in a segment must have similar needs that clearly differ from the needs of another segment.
- Actionable: The company must be able to provide a product or service to the identified segment.
Demographic Customer Segmentation Model
Using observable demographic characteristics is typically the first place companies start when creating a customer segmentation strategy. Although the data is relatively straightforward to get, it’s not enough information on its own. Businesses need to implement additional segmentation models to reach clients effectively.
Demographic customer segmentation forms groups based on demographic information like:
- Age, Gender, and Race
- Family status
- Occupation, Income Level, and Level of Education
- Ethnicity and Religion
In a business-to-client context, demographic customer segmentation is mainly used to present personalized products and services to different segment groups. For example, a clothing store will recommend other products to customers based on age, gender, and interests.

Geographic Customer Segmentation Model
Geographic customer segmentation categorizes a target group by location to ensure marketers better serve clients in a particular area. This model can be broad or narrow, depending on the types of data the company wants to gather.
Companies use segmentation categories like geographic units – countries, regions, time zones, states, and cities – to separate their audience. Others rely on other geographic segmentation measures like climate, population, culture, and language.
Geographic customer segmentation is generally used by companies that sell products and services in multiple countries or time zones. For example, brands may advertise winter apparel in cold areas while targeting swimwear in warmer climates with beaches.
Behavioral Customer Segmentation Model
Behavioral customer segmentation divides consumers according to their behavior patterns, how they interact with the company or brand, and how they make a purchasing decision.
This segmentation category studies the behavioral traits of customers, including their knowledge, use, attitude towards, likes and dislikes, and response to a specific brand, product, service, or promotion.
It’s essential to note that behavioral segmentation doesn’t exist independently from other segmentation categories. Behavioral data confirms conclusions about other segmentation data like Demographic characteristics.
The objective of behavioral customer segmentation is to:
- Identify ways to address the needs or desires of a group of customers.
- Tailor and optimize a product or service to meet those needs or desires.
- Discover opportunities to enhance the customer’s journey.
- Increase clients’ potential value to the business.
- Develop a strategy to improve and increase your customer base.
For example, a company leveraging customer loyalty by establishing a rewards program. Rewards can range from stamp cards, discounts, “buy 3, get the cheapest free,” and many more.
Psychographic Customer Segmentation Model
Companies use psychographic customer segmentation techniques to form groups according to customers’ psychological traits, emotions and thought processes. The method intends to understand “how” customers think and “what” they aspire to become or have in life.
Psychographic customer segmentation includes five segment variables:
- Personality traits
- Lifestyle choices
- Social status
- Attitudes
- AIO (activates, interests, and opinions)
Understanding psychographic factors allows an organization to influence consumption habits based on people’s lifestyles and preferences.
Psychographic customer segmentation is particularly challenging to accomplish without assistance from specialized software. However, you can gather much information by conducting research (surveys, review calls, focus groups, etc.) and monitoring online activity (social media, forums, purchase behavior, reviews, etc.).
For example, an automobile company like BMW caters exclusive cars to people with an upper-class status who desire a premium car with innovative technology.
How to Choose the Right Customer Segmentation Model(s)
Before selecting a customer segmentation model, a company needs to consider and apply the following steps:
- Define concrete marketing goals and variables for a specific campaign.
- Determine the best customer segmentation model to reach a specific segment group, support growth, and achieve set goals.
- Break your goals into customer-centric segmentation projects.
- Identify the best tools and software to collect the needed data for customer segmentation.
- Collect and organize customer data and segment clients into groups.
- Run campaigns and marketing strategies to target selective segment groups.
- Run frequent customer segmentation analyses to test efficacy. Adapt where necessary.
Tips on Doing Customer Segmentation
Additional tips on performing effective and efficient customer segmentation include:
- Create customer personas: Utilize customer data and market knowledge to design customer personas or profiles. Designing marketing content for real individuals is much more accurate than making general assumptions.
Consider details like their demographic and geographic info, background, responsibilities, news sources, site following, preferred communication style, professional history, and attitudes toward certain products, services, and brands. - Track your marketing efforts: Frequently evaluating marketing efforts helps find weak areas that need improvements and the most successful tools and strategies that other members can replicate. Experiment with different platforms, advertising strategies, and target audiences to identify effective marketing approaches.
- Compare with competitor’s strategies: Compare your marketing strategies, offerings, and group segments with your strongest competitor. This will help identify areas where you may fall short of meeting consumer needs. Use the information to improve reaching customers.
- Flexibility is key: Market demands are constantly changing. Remain flexible and be prepared to change your efforts and customer segments to ensure your products remain viable to customers.
Customer Segmentation Benefits to Your Business
Customer segmentation is beneficial for many reasons, including:
- More effective messaging and customer attraction.
- Customer segmentation analysis reveals the segments producing the greatest return on investment, improving customer targeting.
- Improved customer relationships and brand loyalty.
- Enhanced customer experience and increased sales.
- Customer segmentation analysis helps improve product and service quality, usefulness, and viability.
- Higher marketing return on investment (ROI).
- Prepares companies for new market opportunities and potential threats.
Wrap-Up
Customer segmentation strategies help assess the motivations, behaviors, and needs across markets. Segmentation models are created to target specific groups with the best marketing messaging to motivate their purchasing journey.
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution to customer segmentation. Every company needs to create a model that fits its unique customer base.
PIN THIS FOR LATER…
DID YOU FIND THIS INFORMATION HELPFUL? Share the love on social.
Follow us on Pinterest & Instagram!
ANY OTHER BUSINESS ADVICE WE CAN WRITE ABOUT?
Let us know, email us at: Advice@TheBestBusinessAdvice.com

![]()








